CHSH Inequality¶
The CHSH scenario consists of two nonsignaling devices which share randomness in the classical case and entanglement in the quantum case.
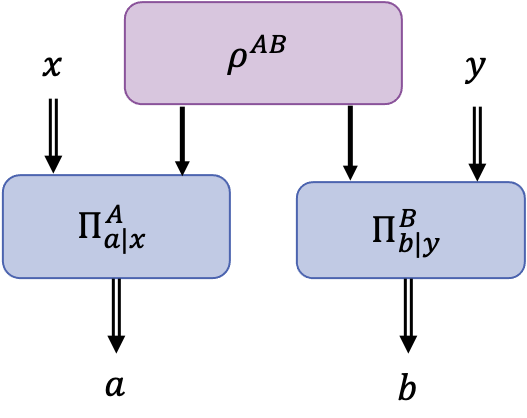
Bipartite Non-Signaling Scenario.¶
The set of classical behaviors is bound by the CHSH inequality [Clauser1969]
where \(\langle A_xB_y \rangle = \text{Tr}[(A_x\otimes B_y )\rho^{AB}]\) is a bipartite correlator for dichotomic observables \(A_x\) and \(B_y\) with eigenvalues \(\pm 1\). Quantum entanglement yields a maximal CHSH score of of \(I_{CHSH}=\leq \beta^Q_{CHSH} = 2\sqrt{2}\) [Cirelson1980].
- qnetvo.chsh_inequality_cost_fn(network_ansatz, parallel=False, **qnode_kwargs)[source]¶
Constructs a cost function for maximizing the score against the CHSH Bell inequality. This inequality is defined as
\[I_{CHSH} = \sum_{x,y\in\{0,1\}}(-1)^{x\cdot y}\langle A_x B_y \rangle\]where \(\langle A_x B_y \rangle = \sum_{a,b\in\{-1,1\}} a\cdot b P(a,b|x,y)\) is the two-body correlator between dichotomic observables \(A_x\) and \(B_y\).
- Parameters:
network_ansatz (NetworkAnsatz) – A
NetworkAnsatzclass specifying the quantum network simulation.parallel (optional bool) – If
True, remote qnode executions are made in parallel web requests.qnode_kwargs (optional dict) – Keyword arguments used only for
pennylane.qnodeconstruction.
- Returns:
A cost function evaluated as
cost(*network_settings)where thenetwork_settingsare obtained from the providednetwork_ansatzclass.
- qnetvo.parallel_chsh_grad_fn(network_ansatz, natural_grad=False, **qnode_kwargs)[source]¶
Constructs a parallelizeable gradient function
grad_fnfor the CHSH cost.The parallelization is achieved through multithreading and intended to improve the efficiency of remote qnode execution.
The natural gradient
\[\nabla_{ng}I_{CHSH}(\vec{\theta}):= g^{-1}(\vec{\theta})\nabla I_{CHSH}(\vec{\theta})\]scales the euclidean gradient \(\nabla\) by the pseudo-inverse of the Fubini-Study metric tensor \(g^{-1}(\vec{\theta})\). The natural gradient of the \(-I_{CHSH}(\vec{\theta})\) cost function is evaluated directly as
\[\begin{split}-\nabla_{ng}I_{CHSH}(\vec{\theta}) &= -\nabla_{ng}\sum_{x,y=0}^1 (-1)^{x \wedge y}\langle A_x B_y\rangle(\vec{\theta}_{x,y}) \\ &= -\sum_{x,y=0}^1 (-1)^{x \wedge y}\nabla_{ng}\langle A_x B_y \rangle(\vec{\theta_{x,y}}) \\ &= -\sum_{x,y=0}^1(-1)^{x \wedge y}g^{-1}(\vec{\theta}_{x,y})\nabla\langle A_x B_y \rangle(\vec{\theta}_{x,y})\end{split}\]where \(\langle A_x B_y \rangle(\vec{\theta}_{x,y})\) is the expectation value of observables \(A_x\) and \(B_y\) parameterized by the settings \(\vec{\theta}_{x,y}\).
- Parameters:
network_ansatz (NetworkAnsatz) – The ansatz describing the network for which the CHSH inequality considered.
natural_grad (optional Bool) – If
True, then the natural gradient is evaluated. DefaultFalse.qnode_kwargs (optional dict) – A keyword argument passthrough to qnode construction.
- Returns:
A parallelized (multithreaded) gradient function
grad_fn(*network_settings).- Return type:
function
Warning
Parallel gradient computation is flaky on PennyLane v0.28+. Intermittent failures may occur.
References¶
Clauser, John F., et al. “Proposed experiment to test local hidden-variable theories.” Physical review letters 23.15 (1969): 880.
Cirel’son, Boris S. “Quantum generalizations of Bell’s inequality.” Letters in Mathematical Physics 4.2 (1980): 93-100.